Introduction
Modaraba is one of the prime modes of Islamic Financial System. The concept of Modaraba has been derived from the teachings of our Holy prophet Hazrat Muhammad (Peace be upon him).
- Definition
- About Modaraba
- Structure of Modaraba
- Types of Modaraba
- Religious Board for Modaraba
- Different Capacities of Mudarib
- Shariah Compliance by Modarabas
- Regulatory Framework for Modaraba
- How to Invest in Modaraba - Floatation of a Modaraba
- Benefits of Investing in Modaraba
- Risks Associated with Investment in Modaraba
Definition
- It is a kind of partnership, wherein one party provides finance to the other, having skill, to carry out any business.
- The party which provides the finance is called the “Rabb-ul-Mal” (the Investor), whereas the other party who puts its management skills and efforts for the Modaraba is called the “Modarib” (the Manager)
About Modaraba
Modaraba or Mudarabah is a special kind of partnership where one partner gives money to another for investing it in a commercial enterprise. The investment comes from the first partner who is called “rabb-ul-mal”, while the management and work is an exclusive responsibility of the other, who is called “mudarib" and the profits generated are shared in a predetermined ratio.
Authenticity in Islam
Hazrat Khadijah gave capital for business and our Holy prophet Muhammad (salAllahu alaihe wassalam) did business from her capital.
Go to TopStructure of Modaraba
Business Model of Modaraba
In Pakistan Modaraba is a unique model of its kind as no such example exists in rest of the world.
- The Modarabas are allowed to offer any financial product or conduct any business based on Islamic concept provided it is Shariah compliant and approved by the Religious Board.
- Modarabas can invest in stock markets, trading of halal commodities, project financing activities etc.
- The Modaraba can raise funds in the form of Certificates of Modaraba and Certificate of Musharaka. Modarabas can also issue Sukuk and Musharaka based TFCs.
- Prospectus of the Modaraba should be approved by the Registrar Modaraba, Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan, after obtaining a certificate from the Religious Board to the business of the Modaraba.
- Modaraba certificates shall be listed on the stock exchange for trading purpose.
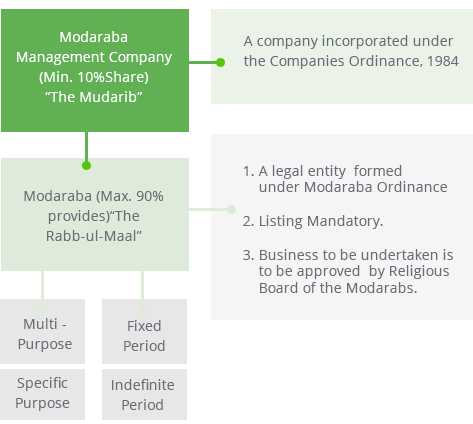
Basic Structure of Modaraba in Pakistan
Modaraba is one of the prime modes of Islamic Financial System. In Pakistan the process of Islamization of the economy was initiated in 1977 and in light of the recommendations made by the Islamic Ideology Council, Government of Pakistan introduced certain changes in the Banking Companies Ordinance and promulgated the Modaraba Companies & Modaraba (Floatation & Control) Ordinance, 1980 to provide a legal framework for Islamic financial system.
This was a major step through which the concept of “modaraba financing” was transformed into an Islamic financial institution in order to allow Modarabas to operate as legal corporate entities. Amongst the other activities, the Modarabas were allowed to undertake Ijarah, Murabahah, Musharakah, Diminishing Musharakah, Salam and Istisna financing activities; trading of Halal Commodities, project financing activities, investment in the stock market and can act as a special purpose vehicle.
Now the Modaraba Companies and Modarabas are operating in Pakistan for the last over 30 years as a unique model and there is no example of any similar legal entities in rest of the world.
The basic structure of a Modaraba operating in Pakistan is given in the following diagram.
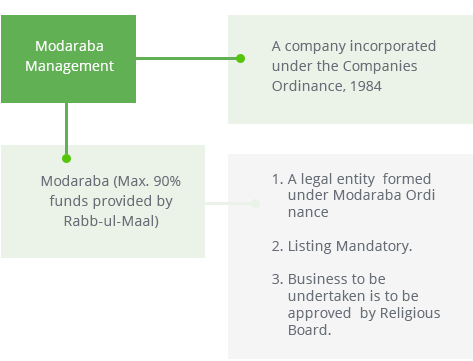
The Companies incorporated under the Companies Ordinance, 1984 and registered with the Registrar (Modarabas), SECP are eligible to undertake floatation and management of Modarabas. The Modaraba or
Modaraba Fund (pool of funds) is created through public subscription (IPO) and listed on stock exchange(s). Generally, a Modaraba can undertake virtually any business activity that is not repugnant to Islam.
Go to TopTypes of Modaraba
Glossary
Mudarib: Working Partner (brings effort)
Ras-ul-Maal: Investment
Rab-ul-Maal: Investor (brings capital)
Wakeel: Agent
Ameen: Trustee
Kafeel: Guarantor
There are two types of Modaraba:
Modaraba Al Muqayyadah (Restricted Mudarabah)
Mudarabah Al Muqayyadah means a restricted modaraba where the Rabb-ul-maal may specify a particular business or a particular place for the mudarib, in which case he shall invest the money in that particular business or place.
Modaraba Al Mutlaqah (Unrestricted Mudarabah)
Modaraba Al Mutalqah means unrestricted modaraba where the Rabb-ul-maal gives full freedom to the mudarib to undertake whatever business he deems fit.
However, he is not authorized to:
- keep another Mudarib or a partner
- mix his own investment in that particular Modarabah without the consent of Rab-ul Maal
The mudarib or mudaribs, as the case may be, are authorized to do anything which is normally done in the course of business. However, if they want to do an extraordinary work, which is beyond the normal routine of the traders, they cannot do so without express permission from the rabb-ul-mal.
Go to TopReligious Board for Modaraba
To achieve the objectives of Islamic business, the Federal Government has established a Religious Board (RB) for the Modarabas.
- The members of Religious Board are well known Shari'ah Scholars of the country and the chairman is qualified to be a Judge of the High Court.
- Religious Board certifies that the business of the Modaraba is not opposed to the injunctions of Islam.
The Federal Government of Pakistan constitutes Religious Board for Modarabas under section 9 of the Modaraba Companies and Modarabas (Floatation and Control) Ordinance, 1980, which comprises of a Chairman and two Shariah Scholars. No Modaraba can operate in Pakistan unless its business and prospectus is cleared from the Religious Board for the Modarabas. All the products and business activities of the Modaraba are approved by the Religious Board for Modarabas with the facilitation of the Modaraba Wing. The following is the composition of the Religious Board constituted by the Federal Government vide notification dated August 30, 2012:
- Former Justice Syed Zahid Husain Bokhari (Chairman) ;
- Mufti Muhammad Saeed Khan (Shariah Scholar); and
- Dr. Muhammad Tahir Mansoori (Shariah Scholar).
Different Capacities of Mudarib
Ameen (Trustee): The capital of Mudarabah is an Amanah in the hand of Mudarib, therefore if any loss incurs to business without negligence of Mudarib, Mudarib will not be liable for that loss. The money given by Rabb-ul-maal (investor) and the assets required therewith are held by him as a trust.
Wakeel (Agent): When Mudarib starts the business, he becomes an Agent of Rabbul-Mal. Therefore, all the business activities will be carried out on behalf of the principal. And if principal (Rabb-ul-Mal) gives any instructions, Mudarib is bound to comply with these instructions.
Shareek (Partner): In case of profit, Mudarib is partner in that business to the extent of his profit share in agreed ratio.
Dhamin (Liable): If Mudarib disobeys the instructions of Rab-ul-Mal or if the enterprise suffers a loss due to his negligence or misconduct, he is liable to compensate the loss.
Ajeer (Employee): If Mudarabah becomes void due to any reason, then Mudarib is Ajeer. He is entitled to get a fee for his services (Ujrat-e-Misl).
Go to TopShariah Compliance by Modarabas
In order to ensure compliance with the Shariah principles, Shariah Compliance and Shariah Audit Mechanism was issued by the Registrar Modaraba vide Circular No. 8 of 2012 dated 3rd February, 2012 after extensive consultation with the Association and market operators which provide a detailed framework for compliance of Shariah principles, investment of competent Shariah scholars for verification of business operations and publication of a certificate of Shariah compliance in the financial accounts of Modarabas.
These guidelines will improve the quality of existing compliance and eliminate the risk of any inadvertent violation of Shariah principles by the Modarabas. It is an important step towards the enhancement of the image of modarabas as a responsible component of Islamic Financial Industry and will help build their business links with Islamic Banks, mutual Funds and Takaful companies.
A ‘Shari’ah Compliance and Shariah Audit Mechanism’ has been issued by the Registrar Modaraba to ensure that all Modarabas are doing their business in conformity with the principles of Shari’ah. A three-tier mechanism for Shariah Compliance has been put in place covering Modaraba, Shariah Advisor and Internal Shariah Auditor.
Shari'ah Compliance at Modaraba Level
Responsibilities include:
- Screening procedure for investment in shares
- Dividend Purification Process
- Haram income not to form part of Modaraba’s income
- Management of Charity
- Investment of surplus funds of Modarabas
Shari'ah Advisor
Responsibilities include:
- Every Modaraba company shall have a Shari’ah Advisor
- Education/Qualification of Shari’ah Advisor
- Functions and Responsibilities of Shari’ah Advisor
- Powers/Responsibilities of the Shari’ah Advisor
- Dispute Resolution
Shari'ah Internal Auditor
Responsibilities include:
- Every Modaraba company shall have a Shari’ah Internal Auditor
- Appointment and Duties of ISA
- Duties of Shari’ah Internal Auditor
- Compliance on the Internal Shari’ah Auditor’s Report
Regulatory Framework for Modaraba
The Modaraba Companies and Modarabas are working under the regulatory framework provided in following laws, rules and regulations.
- Modaraba Companies and Modaraba (Floatation and Control) Ordinance, 1980
- Modaraba Companies an Modaraba Rules, 1981
- Prudential Regulations for Modarabas
- Shariah Compliance and Shariah Audit Mechanism
- Code of Conduct of NBFI & Modaraba Association of Pakistan
- Fit & Proper Criteria for the sponsors, CEO, Directors and Key Executives (2008)
- Shariah Compliance and Shariah Audit Mechanism 2012
The Modaraba Companies & Modaraba (Floatation & Control) Ordinance, 1980:
The Modaraba Companies & Modaraba (Floatation & Control) Ordinance, 1980 provides for matters to registration of modaraba companies and floatation and management and regulations of Modarabas.
The Modaraba Companies & Modaraba Rules, 1981:
In 1981 Modaraba Companies and Modaraba Rules were framed to provide Rules to do the business.
Prudential Regulations For Modarabas 2004:
In 2004 Prudential Regulations for Modarabas were issued. The regulations provide a wide range of risk management tools for conducting the day to day affairs and business of the Modarabas.
Companies Ordinance, 1984:
The affairs of Modarabas are managed through the Modaraba Management Company, which is required to be registered under the Companies Ordinance, 1984. As such, the modaraba company must comply with all the provisions of the Companies Ordinance without any exception. However, where there is consistency in the Modaraba Ordinance and the Companies Ordinance, the provisions of Modaraba Ordinance shall prevail for the Modarabas.
Modaraba Ordinance and Rules defines the main functions of the Registrar Modarabas and the Modarabas, which are:
- Registration and authorization of Modaraba Companies and Modarabas in Pakistan
- Monitoring of Modarabas’ Operations
- Appointment of Auditors
- Accounts and other documents filing requirements
- Issuance of Business Rules and Regulations
- Compliance and Enforcement of Corporate Laws
- Protection of Investors
How to Invest in Modaraba - Floatation of a Modaraba
Key Eligibility Requirements for Registration as Modaraba Company (MC)
- A Company incorporated under the Companies Ordinance, 1984; or a body corporate owned or controlled by the Federal Government or a Provincial Government can apply for the floatation of a Modaraba.
- The Sponsors, Directors and Officers of the MMC and the Modaraba must fulfill the requirement of fit and proper criteria as circulated by the Registrar Modaraba vide circular No. 10/2008 which prescribes that the Promoters/Directors:
- Should be persons of means and integrity
- Should have knowledge and experience of relevant business
- Should not be convicted of fraud or breach of trust or of an offence involving moral turpitude.
- Should have not been adjudged as insolvent or have suspended payment or compounded with their creditors etc.
Permission to Float Modaraba
- A duly registered Modaraba Management Company can apply to the Registrar for grant of permission to float a Modaraba, along with prospectus, feasibility report and other requisite documents as prescribed in the Rules. The Registrar scrutinizes the application and after he is satisfied, submits it to the Religious Board for issue of a certificate on the prescribed Form.
- The Religious Board after having considered that the proposed business of the Modaraba is in accordance with the conjunctions of Islam, approves the application for floatation of a Modaraba.
- After approval of the Board, the Registrar can grant authorization certificate to float a Modaraba.
Investment in Shares/Certificates of Modaraba
- Initial Public Offering: The general public after carrying out due diligence of future prospects may subscribe to certificates of Modarabas when these are first time offered for public subscription.
- Direct Buying from the Market: After the Initial Public Offering, an investor can buy Modaraba Certificates through a broker as these are quoted on the stock exchange(s) just like shares of other listed companies.
Investment in Non-interest Bearing Finance Instruments/ Purchase of Certificates of Musharaka (COM)
- Modarabas may offer various deposit/investment schemes, i.e. Certificates of Musharakah, Certificates of Modaraba, Term Finance Certificates on Musharakah basis, Sukuk etc.,once approved by the Registrar Modaraba.
- The Certificate of Musharaka is on profit-sharing basis. Through this arrangement of Musharaka, a Modaraba raises funds from various investors to fund a project and in lieu of money received issue certificates of Musharaka.
- Such investment scheme is based on profit and loss sharing basis and rate of return varies periodically based on the profitability of the project/business of the Modaraba.
- With the approval of the Registrar (Modarabas), advertisements for such investment schemes are published in which all the information about the scheme, the mechanism of distribution of profit & loss and credit rating of the issuing Modaraba etc. are disclosed.
- No Modaraba can offer such schemes unless it has obtained a minimum investment grade rating, i.e. ‘BBB’ from a registered credit rating agency.
How To Avail The Facilities Offered By Modarabas
All Modarabas regulated by Registrar Modaraba, SECP, have their places of business in major cities of Pakistan, offering a variety of financing, leasing, rental and trading facilities to the Clients. A complete list of the Modarabas is displayed at the website of NBFI & Modaraba Association of Pakistan (association@nbfi-modaraba.com.pk).
Go to TopBenefits of Investing in Modaraba
Following are the advantages of Modaraba:
-
Halal Business
Modaraba is the business model in the financial sector which is based on true Islamic practices duly scrutinized and approved by the members of the Religious Board appointed by the Federal Government. It provides profitable investment opportunities to the stakeholders who are looking for Halal profits on their investments according to Islamic Shariah. -
Diversified Business
The diversity of the Modaraba concept provides a unique universe of business opportunities to the sector, including financing, trading, manufacturing, equipment-rental, participation in property development, project management, portfolio management, imports and exports and distribution business. Such a diverse canvas of activities is not available to any other entity in the Islamic financial regime. -
Tax Benefit
The income earned by the Modarabas, other than the trading modarabas, is fully exempted from income tax provided they distribute 90% of their profits amongst the certificate holders. For trading modarabas, the maximum tax rate is 25 percent. -
Maximum Distributuion of Profits
As an investor of a Modaraba one may expect getting maximum dividends as 90% of the income/profits of the Modaraba are distributed to the certificate holders in order to avail the benefit of tax exemption.
-
Funding and Financial Facilities under Shariah Compliant
Funding and financial facilities under the Shariah compliant modes are provided by Modarabas, on the pattern similar to Islamic banks to the clients.
Risks Associated with Investment in Modaraba
Like every business Modaraba is also exposed to the similar business risks that may have impact on the operation or profitability of the Modaraba. These risks might be internal or external including:
1. Market Risk
Market risk refers to, changes in the value of an investment due to changes of market factors. The prices of and the income generated may decline in response to specific events. These include:
- Direct involvement of companies whose securities are owned by the funds.
- General economic and market conditions.
- Local or global economic instability
- Currency and interest rate fluctuations.
2. Operational Risk
Operational risk can be summarized as human risk; it is the risk of business operations failing due to human error. The prospect of loss resulting from inadequate or failed procedures, systems or policies is termed as Operational Risk. Operational risk will change from industry to industry, and is a significant consideration to make when looking at potential investment decisions. Industries with lower human interaction are likely to have lower operational risk.
3. Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk due to uncertainty in a counterparty’s (also called an obligor’s or credit’s) ability to meet its financial obligations.
4. Regulatory or Shariah Non-Compliance
Risks might arise due to non-compliance of Shariah principles. Compliance with Shariah principles by the Modarabas is mandatory.
The intended investor must keep in mind the above risks and certificate price fluctuation risk which is linked to the market conditions.
Go to Top